Drafting Techniques
Introduction
You should know the techniques of pencil drawing, tracings, and ink tracing
before you attempt to create or revise technical drawings.
Pencil drawings
By far the greater part of all drafting is done in pencil. Most prints or
photocopies are made from pencil tracings; all ink tracings are made from
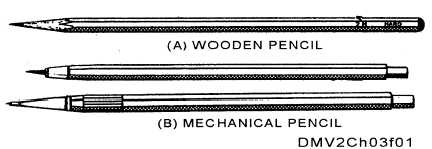
pencil drawings. There are two types of pencils: those with conventional
wood-bonded cases known as wooden pencils and those with metal or plastic
cases known as mechanical pencils.
Figure 3-1 shows an example of a conventional and mechanical pencils.
Figure 3-1.—Conventional and mechanical pencils.
Pencil manufacturers market three types of lead used to produce engineering
drawings; graphite, plastic, and plastic-graphite.
GRAPHITE: Graphite is conventional lead composed of graphite, clay, and
resins. It is available in varying degrees of hardness. The hardest grades are
9H, 8H, 7H, and 6H. Mediums grades are 5H, 4H, 3H, and 2H. Medium
soft grades are H and F. The soft grades are HB, H, and 2B; and the softest
grades are 6B, 5B, 4B, and 3B. The softer grades are not suitable for precise
technical drawing or drafting, but may suffice for freehand technical
sketches.
PLASTIC: Plastic lead was developed particularly for drawing or drafting on
drafting films such as Mylar or vellums. They are available in a limited
number of grades, which do not closely correspond to the degrees of
hardness in conventional graphite leads. Plastic lead has good microform
reproduction characteristics.
Continued on next page
3-6