Basic Rendering Techniques, Continued
Value
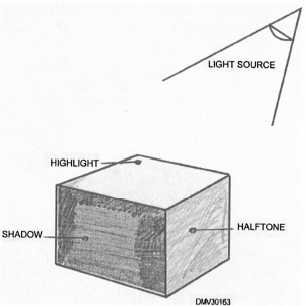
Value is the lightness or darkness of tone illuminated by light. Value
emphasizes the form of an object. As light strikes an object, areas of light,
shade, and shadow appear. Areas struck directly by light may lose local
color entirely. Those areas are called highlights. Areas that receive no
direct light and appear close to the local color are called halftones.
Areas in
the shadows or that have a shadow cast over them are darker than the local
tone.
Figure 3-26 shows a cube with tonal values.
Figure 3-26.—Tonal values of a cube.
Using light,
You can use light, tone, and value instead of lines for defining shapes or
tone, and value
objects. Select a set or scale of values in the medium of your choice.
Compare this scale of values to the natural values of the object.
It is
sometimes helpful to view the object through partly closed eyes to eliminate
detail. Separation between value areas will depend upon the intensity of the
light source. Bright light produces well-defined value separations, soft light
has the opposite effect. Angular or planed edges have sharply defined value
areas. Rounded areas are softly defined and gradual.
Hard surfaces have
values separated to the extreme while textured areas appear grainy.
Continued on next page
3-22