ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
Isometric projection is the most frequently used
type of axonometric projection, which is a method
used to show an object in all three dimensions in a
single view. Axonometric projection is a form of
orthographic projection in which the projectors are
always perpendicular to the plane of projection.
However, the object itself, rather than the projectors,
are at an angle to the plane of projection.
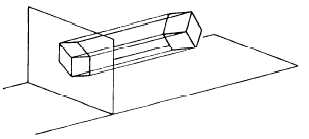
Figure 3-6 shows a cube projected by isometric
projection. The cube is angled so that all of its surfaces
make the same angle with the plane of projection. As a
result, the length of each of the edges shown in the
projection is somewhat shorter than the actual length of
the edge on the object itself. This reduction is called
foreshortening. Since all of the surfaces make the angle
with the plane of projection, the edges foreshorten in
the same ratio. Therefore, one scale can be used for the
entire layout; hence, the term isometric which literally
means the same scale.
VIEWS
The following pages will help you understand the
types of views commonly used in blueprints.
MULTIVIEW DRAWINGS
The complexity of the shape of a drawing governs
the number of views needed to project the drawing.
Complex drawings normally have six views: both
ends, front, top, rear, and bottom. However, most
drawings are less complex and are shown in three
views. We will explain both in the following
paragraphs.
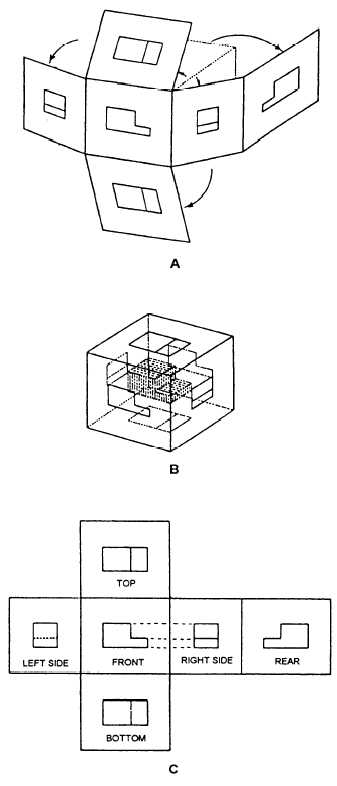
Figure 3-7 shows an object placed in a transparent
box hinged at the edges. With the outlines scribed on
each surface and the box opened and laid flat as shown
in views A and C, the result is a six-view orthographic
Figure 3-7.—Third-angle orthographic projection.
Figure 3-6.—Isometric projection.
3-3