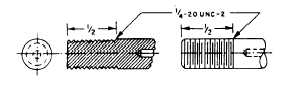
them. Now look at figure 4-12. The left side shows a
thread profile in section and the right side shows a
common method of drawing threads. To save time, the
draftsman uses symbols that are not drawn to scale. The
drawing shows the dimensions of the threaded part but
other information may be placed in “notes” almost any
place on the drawing but most often in the upper left
corner. However, in our example the note is directly
above the drawing and shows the thread designator
“1/4-20 UNC-2.”
The first number of the note, 1/4, is the nominal size
which is the outside diameter. The number after the first
dash, 20, means there are 20 threads per inch The letters
UNC identify the thread series as Unified National
Coarse. The last number, 2, identifies the class of thread
and tolerance, commonly called the fit. If it is a
left-hand thread, a dash and the letters LH will follow
the class of thread. Threads without the LH are
right-hand threads.
Specifications necessary for the manufacture of
screws include thread diameter, number of threads per
inch, thread series, and class of thread The two most
widely used screw-thread series are (1) Unified or
Figure 4-12.—Outside threads.
National Form Threads, which are called National
Coarse, or NC, and (2) National Fine, or NF threads.
The NF threads have more threads per inch of screw
length than the NC.
Classes of threads are distinguished from each other
by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance specified.
Classes of thread were formerly known as class of fit, a
term that will probably remain in use for many years.
The new term, class of thread, was established by the
National Bureau of Standards in the Screw-Thread
Standards for Federal Services, Handbook H-28.
Figure 4-13 shows the terminology used to describe
screw threads. Each of the terms is explained in the
following list:
HELIX—The curve formed on any cylinder by a
straight line in a plane that is wrapped around the
cylinder with a forward progression.
EXTERNAL THREAD—A thread on the outside
of a member. An example is the thread of a bolt.
INTERNAL THREAD—A thread on the inside of
a member. An example is the thread inside a nut.
MAJOR DIAMETER—The largest diameter of an
external or internal thread
AXIS—The center line running lengthwise through
a screw.
CREST—The surface of the thread corresponding
to the major diameter of an external thread and the minor
diameter of an internal thread.
Figure 4-13.—Screw thread terminology.
4-4